Description
A lithium-ion single-cell charging module is a small circuit designed to safely charge a single Li-ion (or LiPo) cell, typically with a nominal voltage of 3.7 V (fully charged at ~4.2 V).
The most common and inexpensive example is the TP4056 module.
Key Features
-
Input voltage: Usually 5 V (USB or regulated supply)
-
Charge voltage: 4.2 V (fixed)
-
Charge current: Adjustable (default 1 A for TP4056; set with resistor)
-
Protection:
-
Some modules include overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit protection (via DW01A + FS8205 MOSFETs).
-
Others are bare charger boards without protection, intended for cells that already have a built-in protection circuit
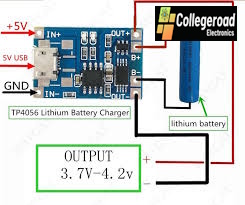
single cell charging module
-
Things to Keep in Mind
-
Never charge a Li-ion cell without a proper charger—overcharging can cause fire or explosion.
-
Ensure good heat dissipation for modules like TP4056 if charging at 1 A.
-
If your cell has no built-in protection board, use a module with protection.
-
Charging current should ideally be ≤ 0.5–1 C of battery capacity.
Example: For a 2000 mAh cell, charge at ≤ 1–2 A (safer at ~1 A).
Module performance:
The input voltage: 4.35-6 v (recommended voltage 5 v)
Charge cut-off voltage: 4.2 V + / – 1%
Maximum charging current output: 1000 ma
The battery overcharge protection voltage: 4.28 V
Battery overcharge lifting voltage: 4.00 V
The battery discharge protection voltage: 3.0 V
Battery discharge termination voltage: 3.2 V
Battery: over-current protection current 3 a
The board size: about 2.5 * 1.65 CM
Light state: no load the light not bright, red light for recharging, is full of green light.





















 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart. 
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.